Ivan Saloň, Peter Ševčenko, František Štěpánek
Glucan particles are purified cell walls from Saccharomyces cerevisiae (baker’s yeast). They are 85% 1,3-D-glucan polymers, 2% chitin, and 1% protein and lipids, with the rest of the ash and moisture. They are hollow and porous microspheres with the size from 1 to 5 μm. The 1,3-β-glucan outer shell is able to provide receptor-mediated uptake by phagocytic cells which are expressing β-glucan receptors and therefore the glucan particles have been used for macrophage-targeted delivery. β-glucans are polymers of β-(1,3)-D-glucose with or without β-(1,6)-D-glucose in side chains.
Our targets of research are to develop a new methods for the creating of glucan particles composite materials with paramagnetic properties useful for the MRI, making the new chemical modifications of the glucan particles shells used in the fluorescence bioimaging and drug delivery.

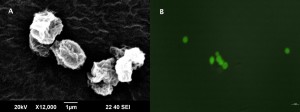
A- suspension of composite magnetic glucan microparticles, B- composite magnetic glucan microparticles assembled due to the presence of magnetic field
Publications
- Saloň I., Hanuš J., Ulbrich P., Štěpánek F., “Suspension stability and diffusion properties of yeast glucan microparticles”, Food Bioprod. Process. 99, 128-135 (2016)