Petra Haufová, František Štěpánek
Layer-by-Layer method (LbL) is a thin film fabrication technique. The films are formed by depositing alternating layers of oppositely charged materials. The layers can be performed in different ways e.g. dip coating, spin-coating, spray-coating. Various materials can be deposited by LbL method including polyions, metals, ceramics, nanoparticles, and biological molecules.
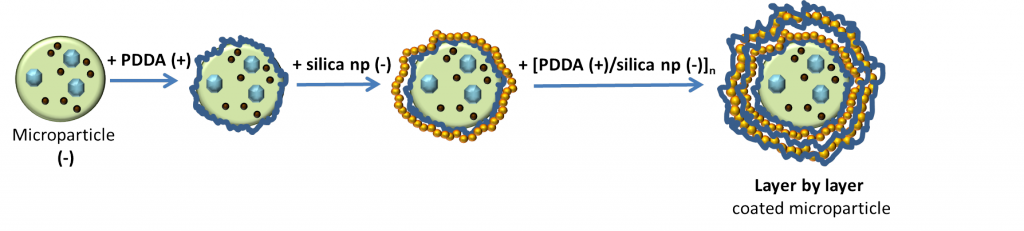
The aim of our work is to produce silica-coated alginate particles with specific controllable shell structure for applications in drug and other chemicals delivery. The silica shell can be made by electrostatic Layer by Layer assembly of silica nanoparticles on the surface of alginate microparticles. Alginate particles as well as silica nanoparticles are negatively charged, therefore the positively charged polyelectrolyte Poly(dimethyldiallylamonium chloride) (PDDA) is used as a “binder”.
We use dip coating with following steps:
- Poly(dimethyldiallylamonium chloride) – PDDA (positively charged)
- Washing
- Silica nanoparticles – silica np (negatively charged)
- Washing
Then 1.-4. are repeated till the coating reachs the desired thickness.
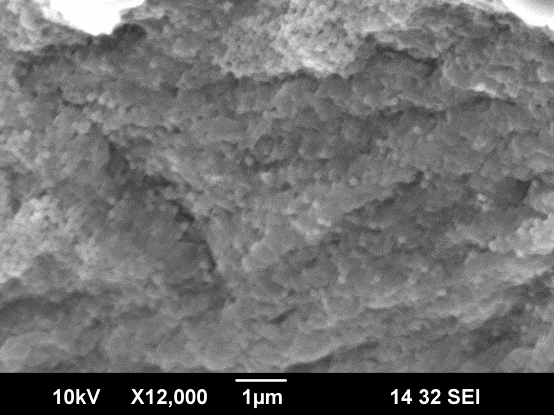
Characterisation of LbL film deposition is done by image analysis (optical microscopy, scanning electron microscopy and laser scanning confocal microscopy) and by Quartz Crystal Microbalance – QCM.
LbL coating provides the additional benefits such as
i) enhancement of mechanical properties of gel microparticles;
ii) control of diffusion and porosity;
iii) enabling other surface modifications for specific adhesion.

![Thickness of [PDDA/silica nanoparticles] layers calculated from the QCM measurement.](https://www.chobotix.cz/wp-content/uploads/2013/02/lbl-graf.png)